FAP is a psychological concept. It was proposed by:
- John Dollard,
- Leonard Doob,
- Neal E. Miller,
- O. Hobart Mowrer,
- Robert Sears
This hypothesis suggests that:
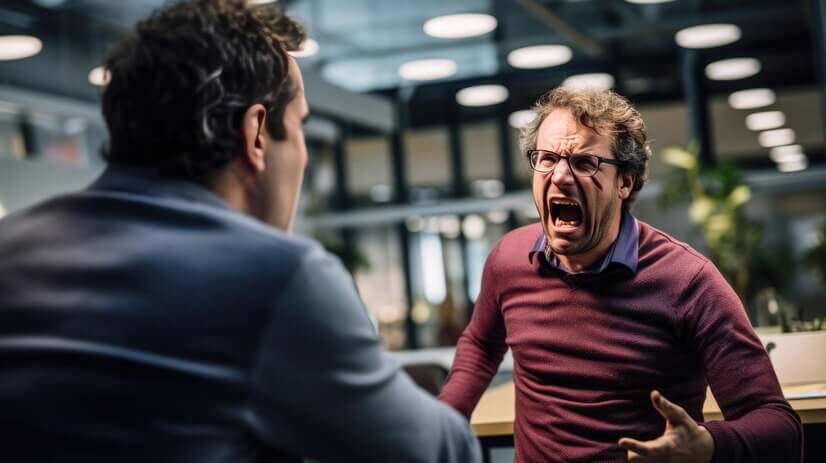
- Frustration leads to aggression
- Implying a causal relationship between the two:
- While it’s often referred to as the:
- Frustration-Aggression Principle
- While it’s often referred to as the:
- Initially it was proposed as a hypothesis.
- Later research has both supported and refined this idea
- The original formulation was indeed put forth by Dollard, Doob, Miller, Mowrer, and Sears in 1939.
FAP: Understanding the Concept

- When someone is prevented from achieving a desired goal, they experience frustration, which can trigger aggressive behavior.
- This principle highlights the link between frustration and aggression in human behavior and mental state.
- It has been influential in understanding various aspects of social behavior and conflict resolution.
- Frustration is an inevitable part of life.
- Whether it’s encountering obstacles in our endeavors or facing challenges in our professional lives, we’ve all experienced moments of frustration.
FAP: The Origin
- The Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis emerged during a time of growing interest in understanding the underlying causes of aggression.
- Against the backdrop of societal unrest and the looming shadow of World War II, psychologists sought to unravel the complexities of human behavior, particularly about aggression.
- Dollard, Doob, Miller, Mowrer, and Sears proposed the hypothesis that frustration serves as a precursor to aggressive behavior.
- They argued that when individuals are thwarted in their efforts to achieve a desired goal, they experience frustration.
- This frustration, in turn, triggers a readiness to aggress.
Key Concepts of FAP
The Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis consists of several key concepts. It makes the relationship between:
- Frustration
- Aggression
Frustration:
- Frustration arises when individuals encounter obstacles or barriers that prevent them from reaching their goals.
- This frustration can stem from various sources, including external constraints.
- It can also arise from interpersonal conflicts or internal obstacles.
Aggression:
- Aggression refers to behavior intended to cause harm or injury to others, either physically or psychologically.
- It can manifest in diverse forms.
- These forms range from verbal hostility to physical violence.
Catharsis:
- One aspect of the Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis is the notion of catharsis.
- Catharsis refers to the release of pent-up aggression through non-harmful outlets.
- While initially proposed as a potential mechanism for reducing aggression, subsequent research has called into question its effectiveness.
FAP: Implications and Critiques
Implications
- The Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis has significant implications for understanding various aspects of human behavior.
- These aspects include interpersonal conflict, social unrest, and aggression-related phenomena.
- However, it has also faced criticism and refinement over the years.
Critics
- Critics argue that the relationship between frustration and aggression is more complex than initially proposed.
- This complexity is influenced by factors such as individual differences, situational variables, and cognitive processes.
- Additionally, research has highlighted the role of learned behavior, social norms, and cultural factors in shaping aggressive responses to frustration.
Furthermore:
- The Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis highlights the link between frustration and aggression
- It does not account for the myriad ways in which individuals may respond to frustration, including:
- Adaptive coping strategies,
- Problem-solving approaches, or withdrawal
Conclusion
- The Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis remains a foundational concept in the study of human aggression.
- It offers valuable insights into the interplay between frustration and aggressive behavior.
- Its origins can be traced back to the work of Dollard, Doob, Miller, Mowrer, and Sears,
- Subsequent research has both supported and refined its central tenets.
- From interpersonal violence to international conflicts:
- Understanding the dynamics of frustration and aggression is essential for:
- Addressing a wide range of societal challenges
- Understanding the dynamics of frustration and aggression is essential for:
- By exploring the complexities of human behavior through the Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis, psychologists continue to deepen our understanding of:
- What drives individuals to engage in aggressive acts
- How can these tendencies be mitigated or redirected toward more constructive ends?
FAP: Call to Action
- Raise your dimensions to explore:
- The intricacies of human behavior by:
- Uncovering the complexities of:
- Frustration
- Aggression
- Uncovering the complexities of:
- The intricacies of human behavior by:
- Unravel the nuances of human behavior and gain insights that can inform your understanding of the world around you.