2.4 GHZ vs 5GHZ wifi
Which Band Should You Use?
Is your Zoom call lagging or Netflix buffering even when your internet speed is fine?
You might be connected to the wrong Wi-Fi band. Choosing between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz can be the difference between flawless video and frustrating disconnection.
Introduction
Wi‑Fi runs primarily on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. While many routers support both (dual-band), most users overlook the significant impact this choice has on:
- Speed
- Stability
- Interference
- Device compatibility
In this expert guide, we’ll explore:
- Key differences in range and speed
- Pros & cons for each band
- Ideal use-cases and device recommendations
- Visual data to clarify performance
- Smart setup and optimization tactics
By the end, you’ll be equipped to choose which band suits your home network needs—like a pro.
Frequency Overview: What It All Means

| Feature | 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
| Wavelength | Longer – better at passing through walls | Shorter – faster but weaker penetration |
| Channels | 14 total, only 3 non-overlapping | ~30 non-overlapping channels; supports bonding |
| Common Use | IoT, general browsing, long-range | Streaming, gaming, file transfers |
| Interference | High (microwaves, Bluetooth, neighbors) | Low — fewer competing signals |
Speed & Range: What You’re Actually Getting
- 2.4 GHz: Speeds up to ~450–600 Mbps; works over ~150 ft indoors
- 5 GHz: Can exceed 1 Gbps, but works best within 75 ft
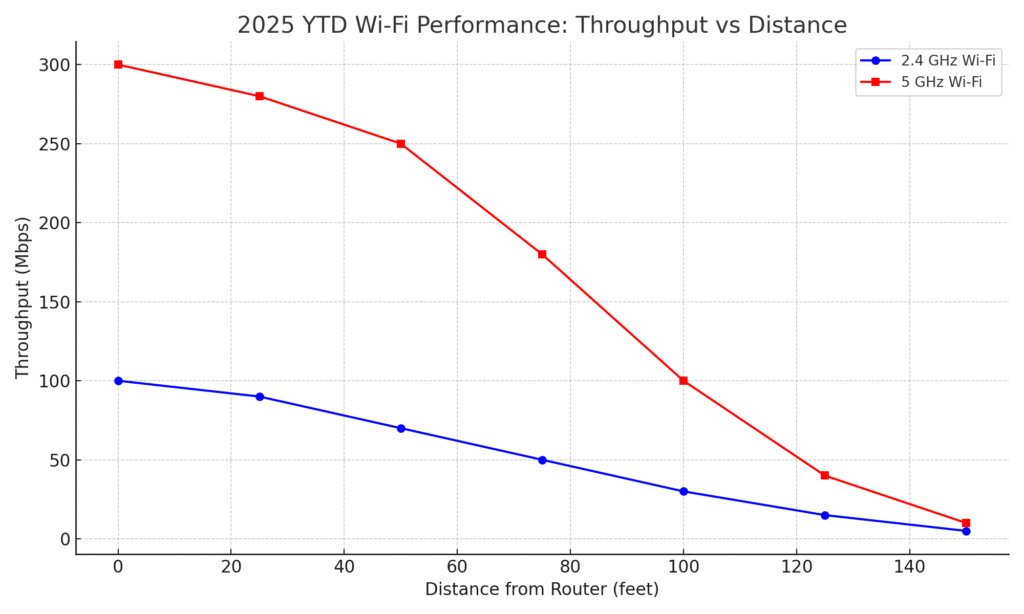
- Test Example: At 120 ft distance, 5 GHz provides ~250 Mbps vs only ~10 Mbps on 2.4 GHz
Conclusion: Use 5 GHz for speed, 2.4 GHz for coverage.
Interference & Congestion
- 2.4 GHz: Shared with microwaves, Bluetooth, baby monitors — prone to heavy interference
- 5 GHz: Less crowded; enjoys non-overlapping channels and
Tip: In dense environments (apartments), 5 GHz can outperform even for long-distance use due to fewer signal clashes.
2.4 ghz vs 5ghz wifi: Device Compatibility & Power Usage
- Universal support on 2.4 GHz → ideal for legacy and IoT devices
- NEWER devices (phones, laptops) support both bands
- Power use: 2.4 GHz is more battery-efficient — better for sensors and battery-powered gadgets
Real-World Scenarios
- Smart home sensors (e.g., thermostats) → use 2.4 GHz for stable, low-energy communication
- 4K streaming or gaming PCs → use 5 GHz for highest throughput
- Wandering devices (laptops, phones) → either, based on where they roam
- Old/non-5 GHz compatible gadgets → must stay on 2.4 GHz
Visual Comparisons
2025 YTD Wi‑Fi Performance
Line graph comparing 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz throughput over distance and interference levels
Band Usage Chart
Stacked chart:
- 2.4 GHz: Low speed, high coverage, high congestion
- 5 GHz: High speed, lower coverage, low congestion_
(accounting for channel bonding and device density)
Recommend tools: Canva, Flourish, Excel.
2.4 ghz vs 5ghz wifi: Optimizing Your Setup (Expert Tips)
- Use a dual-band router and create separate SSIDs (e.g., “Home‑2.4” & “Home‑5”)
- Band steering: modern routers can auto-connect devices to optimal band
- Optimize channels: use Wi‑Fi analyzers to select non-overlapping lines
- Adjust bandwidth: use 40 MHz+ channel bonding on 5 GHz for heavy usage
- Positioning: router in central location; consider mesh extenders to cover blind spots
Expert Insights & Original Insight
- Emerging trend: Wi‑Fi 7 adds better interference handling in 2.4 GHz—allowing channel bonding resilience
- Infra tip: Algorithmic quality-of-service (QoS) systems now prioritize real-time traffic on 5 GHz—ideal for gaming/streaming
When to Use Each Band: Quick Guide
| Situation | Recommended Band |
| 4K video streaming/gaming | 5 GHz |
| Fax-though walls, long range needed | 2.4 GHz |
| IoT and battery devices | 2.4 GHz |
| Mixed device household | Use dual-band w/ steering |
| Dense Wi-Fi environments (apartments) | 5 GHz |
FAQ related to 2.4 ghz vs 5ghz wifi
Q: Can 5 GHz reach the whole house?
A: Yes—if your router is central and the home isn’t heavily obstructed. Otherwise, mesh or extenders are helpful.
Q: Does every device need 5 GHz?
A: No — smart bulbs, sensors, and legacy devices often only use 2.4 GHz, which is fine for their needs.
Q: Will 2.4 GHz always be slow?
A: In busy areas, yes—due to interference. But it’s perfect for low-bandwidth tasks in less dense environments.
2.4 ghz vs 5ghz wifi: Conclusion
Choose 2.4 GHz for range and compatibility, 5 GHz for speed and stability. Ideally, use a dual-band setup with smart steering to let devices connect optimally, maximizing performance across all your home tech.
Read more about Technology on our website raiseyourdimensions.com







